Imagine this: You’re in charge of project control and project management for your company, starting with the launch of a major product update. A product update set to define your company vision.
The stakes are high. All eyes are on you. Every decision counts, every resource allocated has to yield maximum returns, and every deadline needs to be precise. There is no room for error in this project. How do you ensure nothing goes wrong and the project is a success?
Two words: Project control. With effective project control measures, you can reduce potential issues when implementing a project.
How? This comprehensive guide will give you your answers. Explore the methodologies and principles governing project control, the requisite tools, processes, and insights essential for overcoming the complexities inherent in project management. Let’s dig in.
Boost your team’s efficiency with Hubstaff's productivity tools
Introduction to project control
First things first. What is project control in project management?
Project control in project management involves implementing tools and techniques to track the project’s progress against the planned objectives and identifying any deviations or variances. By exercising effective project control, project managers can proactively address issues, mitigate risks, optimize resource utilization, and ultimately increase the likelihood of project success.
Understanding project control
Definition and objectives
Project control is the process of monitoring and evaluating all project aspects to ensure a successful completion within the predefined parameters, including cost, scope, schedule, and quality.
First, let’s look at project control using an example of a popular brand: Apple Inc.
With its innovative products and user experiences, Apple has delivered successful projects by meticulously managing every aspect of product development.
Consider the launch of the iPhone. The company has a well-planned pre-launch process, employing strict project control measures to oversee every product development phase, from design to marketing.
By closely monitoring each project stage, the brand ensures that the product meets high-quality standards and customer expectations.
Objectives of project control
- Primary objective: Project regulation
Scheduled outcomes are defined in the project planning phase. Regulation in project control aims to monitor and compare the actual project output delivered.
- Secondary objective: Resource conservation
Resource conservation aims to ensure all resources related to projects, including human resources, finances, and materials, are protected.
- Tertiary objective: Facilitate decision making
Project control measures require generating precise reports that include information about the project plan, budget, schedule, etc.
Project control vs project management
These two concepts have similar functions. However, they are different at their core. In short, here is the difference between these two.
Project Control involves monitoring and regulating project performance to align with the objectives and constraints defined in the project planning phase.
On the other hand, project management covers everything — from project proposal and planning to execution to managing projects. This process includes handling risks, schedules, and resources.
Now, let’s do a comparative analysis.
| Aspect | Project control | Project management |
| Focus | Monitor and regulate project performance | Planning, execution, and oversight of the entire project |
| Objectives | Ensure alignment with planned objectives and constraints | Achieve project goals within specified parameters |
| Activities | Track progress, identify deviations, implement corrective actions | Plan, organize, coordinate, direct, and control resources and activities |
| Scope | Narrow focus on performance monitoring and regulation | Broad scope covering all aspects of project execution |
| Timeframe | Continuous throughout the project lifecycle | From project initiation to completion |
| Responsibility | Primarily responsibility of project controllers | Shared responsibility among the project team and managers |
The project control process
The project control process is essential for overseeing and managing all aspects of a project’s execution. But don’t worry; it only involves four simple steps.
The 4 steps in the project control process
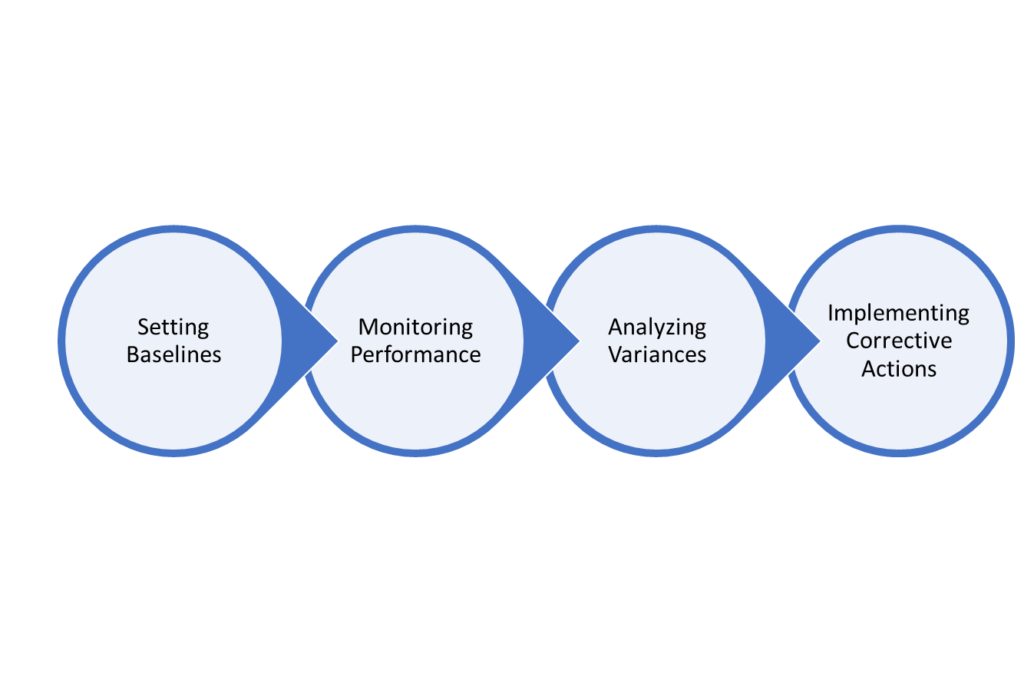
1. Setting baselines
First, you need to establish baseline plans for scope, schedule, budget, quality, and other relevant project parameters. You can measure a project’s performance using these baselines as reference points.
2. Monitoring performance
Then, once a project starts, project control ensures continuous progress monitoring against the baselines established in the first step. The monitoring process tracks aspects like milestones, key project metrics, and deliverables, ensuring a project is on track.
3. Analyzing variances
Now, identifying any deviations from the goals set at the start of your project is crucial. This step isn’t easy, but it enables you to easily predict potential issues and ensure they don’t affect the project’s objectives.
4. Implementing corrective actions
Lastly, take appropriate action, such as reallocating resources, revising schedules, or adjusting project plans to bring the project back on track.
These four steps are iterative in a project lifecycle to ensure it stays on course and achieves the objectives within the defined constraints. But, our journey into project control is just beginning.
Types of controls in project management
There are six types of project controls in project management, as seen below.
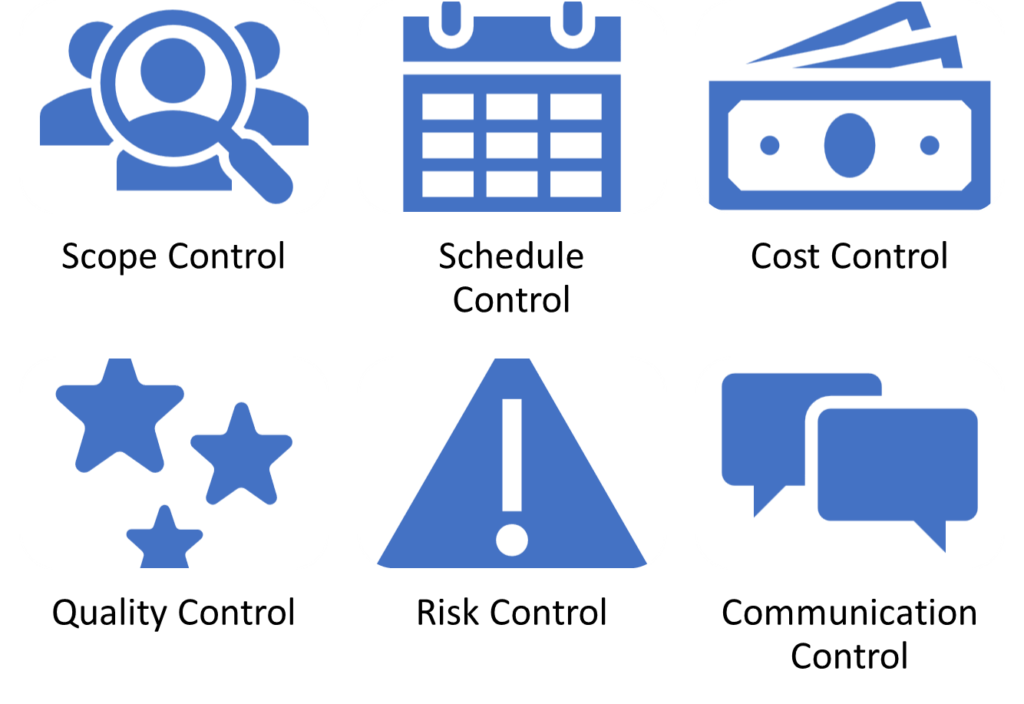

Let’s cover them quickly, starting with scope control.
- Scope control focuses on managing changes to the project scope.
The goal: To ensure the project delivers the outcomes defined in the planning phase. - Schedule control enables continuous monitoring and management of the project schedule.
The goal: To ensure timely completion of all project activities. - Cost control focuses on monitoring and managing all costs related to a particular project.
The goal: To ensure project completion in the approved budget. - Quality control ensures project deliverables meet the required quality standards.
The goal: To address any deviations from the defined quality requirements. - Risk control involves identifying, assessing, and managing project risks.
The goal: To mitigate and minimize potential project risks. - Communication control fosters, monitors, and ensures smooth, transparent communication between all project stakeholders.
The goal: To ensure that stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle, then you can ensure you will have buy in.
Now that you understand the project control process, let’s talk about how to implement it.
Implementing project control systems
Implementing project control systems involves establishing frameworks and tools to monitor and regulate various aspects of a project, such as scope, schedule, budget, and quality. These systems enable project managers to track progress, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions to align the project with its goals.
First, let’s cover the key elements of project control.
Components of a project control system
These key components of project control are the crux of nailing your project management.
- Estimating: Before you start a project, it’s crucial to understand and predict the required project resources, such as time, costs, materials, etc.
- Scheduling: Scheduling involves developing a project plan with information on project duration and dependencies.
- Cost control: With a specific budget allocated to a particular project activity, monitoring and managing project costs to ensure completion within the set budget is crucial. Cost control prevents cost overruns.
- Budgeting: Budgeting refers to allocating a budget to all project-related activities. The budget allocated to each project activity is based on the total cost estimated for the project. A well-defined project budget ensures effective cost control.
These key components work together within a project control system in project management to ensure effective planning, execution, monitoring, and control of project activities, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Importance of project control
Project management is vital. But, various aspects build the road to ensure successful execution. One aspect is project control, so let’s talk about it.
Project control plays a vital role in the success of a project. The importance of project control in project management through various aspects:
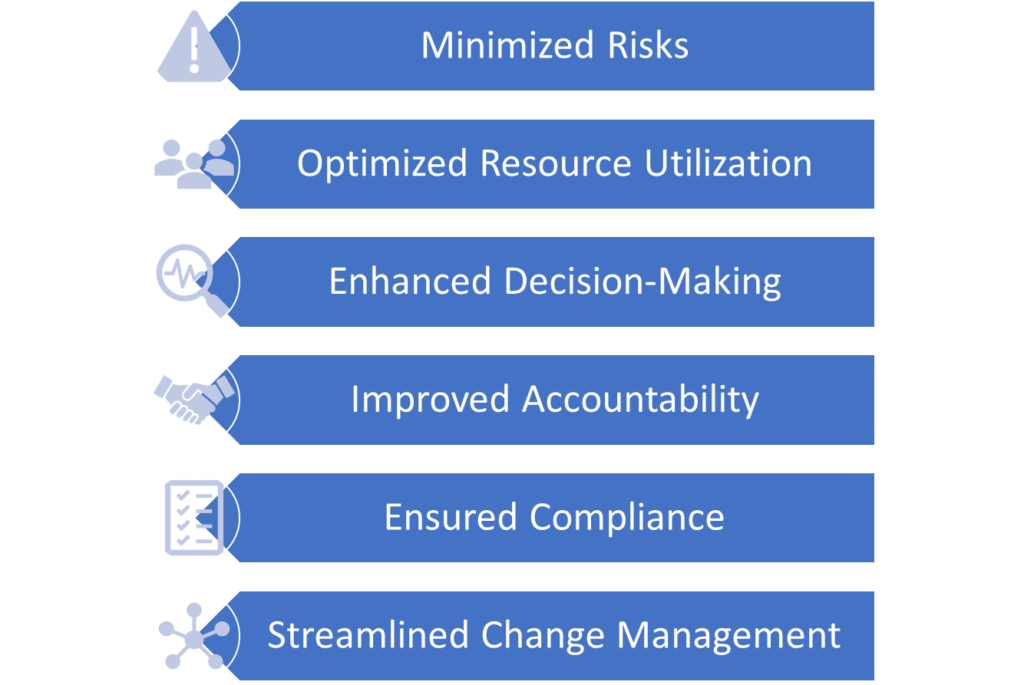
Minimized risks
Project control measures proactively and continuously monitor project risks. This makes identifying and solving potential risks simple, so the project stays on schedule and is completed on time.
Optimized resource utilization
Effective project control involves monitoring resource allocation and utilization, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and effectively to maximize project value while minimizing waste and redundancies.
Enhanced decision-making
Project control provides stakeholders with timely information about project performance, enabling informed decision-making. It helps identify issues, evaluate alternatives, and select appropriate courses of action to address challenges and opportunities.
Improved accountability
Through clear documentation of project plans, baselines, and performance metrics, project control helps establish accountability among project team members and stakeholders.
Ensured compliance
Project control helps ensure compliance with regulations, standards, and policies. It also ensures that project activities are conducted ethically and in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Streamlined change management
Project control provides a structured approach to change management. It ensures that changes are correctly evaluated and executed without disrupting project progress.
Project control techniques and tools
Project control tools and techniques encompass a range of methodologies and software that can monitor, track, and manage project progress. Additionally, these tools can help determine project risks, facilitating effective decision-making and ensuring projects stay on schedule and within budget.
So, let’s get started by looking at common project control techniques.
Effective project control techniques
Effective project control techniques are essential for monitoring, evaluating, and regulating project activities to ensure successful project outcomes. Here are some fundamental methods:
Work breakdown structure (WBS)
WBS breaks the project into smaller, manageable tasks, facilitating better control and monitoring. Then, it helps identify work packages, define deliverables, assign responsibilities, and enable efficient project progress tracking.
Gantt charts
Gantt charts are visual representations of project schedules. They include critical aspects such as task duration, dependencies, and sequences. Generally, people will use a mix of charts (including Gantt and Kanban) to display their project status.
Kanban
Kanban is another project control tool in project management that makes work visualization, workflow optimization, and task prioritization easier, especially for large projects. Equally important is the async communication that Kanboard boards enable.
By providing transparency into project status, Kanban ensures effective project control so leaders can prioritize tasks, improve employee engagement, and speed up project delivery.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Establishing relevant KPIs enables measuring project performance against predefined objectives. KPIs may include cost variance, schedule variance, quality metrics, and customer satisfaction.
Tools for project control
Tools are crucial in facilitating a project control process in project management by providing functionalities for planning, monitoring, analyzing, and communicating project-related information. But with so many tools out there, where should you start? Here are some standard tools used to enable project control processes:
Time tracking software
Tracking the time taken to complete project tasks is crucial in meeting deadlines efficiently. The ideal way to achieve this is by leveraging time tracking software like Hubstaff. With the help of these tools, it’s easier to track the time taken to complete tasks, giving a clear idea and enabling team members to ensure the project stays on schedule and all deadlines are met.
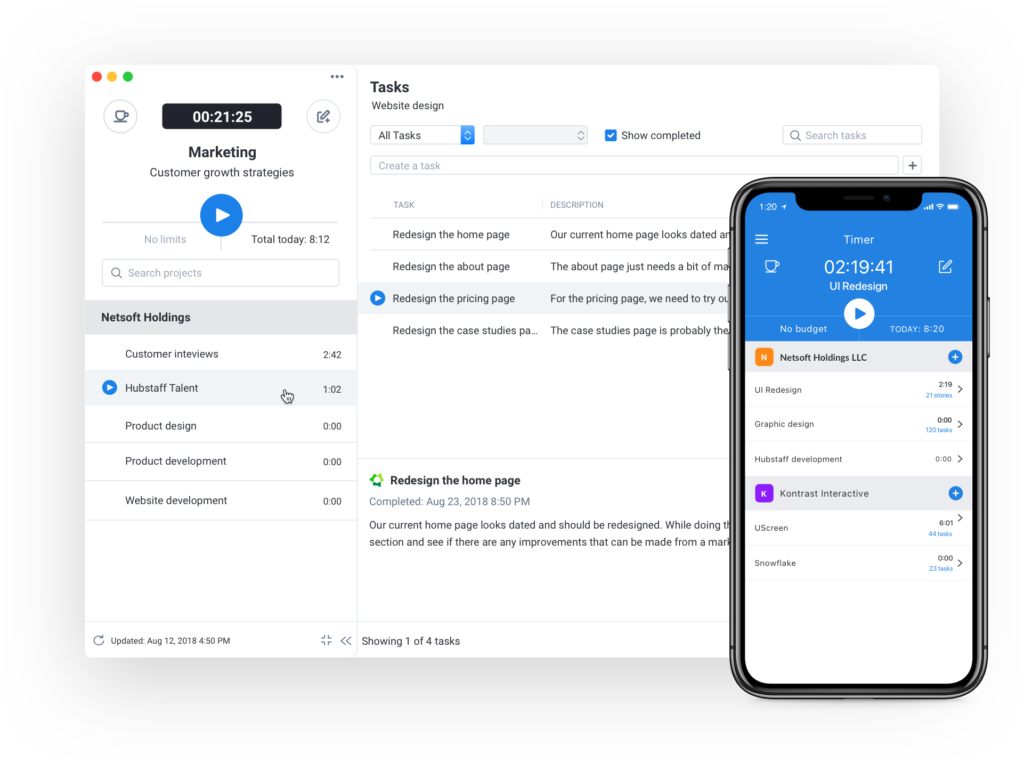
Collaboration platforms
Collaboration platforms such as Slack and Zoom facilitate communication, document sharing, and collaboration among project stakeholders. Mostly, these platforms provide a centralized place for project documentation, discussions, and updates to be stored. Additionally, they allow for video meetings, private messaging, and group threads about project status.
Project management software
Project management tools, like Hubstaff Tasks, offer features that help you streamline the entire project process from initiation to completion. It’s a centralized platform that makes assigning, monitoring, evaluating, and managing projects easy while enabling effective stakeholder communication.
Earned value management (EVM) tools
Lastly, dedicated EVM tools integrate scope, schedule, and cost data to calculate KPIs, such as earned value, planned value, and actual cost, and can provide insights into project performance and variance analysis.
By effectively leveraging these tools, project managers can streamline project control processes, improve visibility into project performance, and further ensure project success within the defined constraints.
Project control in practice
Let’s look at a few project control examples and how they ensured success. Additionally, we will cover how project control is used in different industries.
Real-world examples
Now, it’s time to consider project control in the real world, not just as a concept. First, let’s start with SpaceX.
SpaceX Falcon Heavy Launch
SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy launch exemplifies effective project control in the aerospace industry. The project involved meticulous planning, scheduling, and coordination to launch the world’s most powerful operational rocket.
So, Space X implemented project control techniques like EVM to monitor progress and manage costs throughout the development and launch phases.
Additionally, risk management played a crucial role in identifying and mitigating potential hazards, ensuring a successful and safe mission.
London Crossrail Project
The best example of project control in project management for large-scale infrastructure development is the Crossrail project in London.
This construction project worked on tight schedules and endured extensive stakeholder coordination while overcoming complicated engineering challenges.
So, how did the team complete this project? By utilizing project control techniques, such as Critical Path Method (CPM) scheduling. They used the method to manage the project timeline and ensure timely milestone completion.
Moreover, changes in the control process were implemented to address scope changes and mitigate potential project schedule and budget disruptions.
Project control in different industries
Project control is vital across various industries to ensure successful project outcomes. Now, let’s explore its application in four sectors: construction, information technology (IT), health care, and automotive.
- Construction: Involves managing elements such as scheduling, budgeting, and resource allocation to ensure projects are done on time. Specifically, project control focuses on budget constraints while maintaining quality and safety standards.
- IT: Focuses on overseeing software development, system implementation, and IT infrastructure projects. Ultimately, project control ensures alignment with business objectives, managing technological risks, and delivering solutions on time and within budget.
- Health care: In the health care industry, project control is focused on coordinating complex projects such as hospital expansions, implementing new health care technologies, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Mostly, the focus is to enhance patient care and operational efficiency.
- Automotive: The automotive industry uses project control to manage manufacturing processes and supply chain operations to deliver high-quality vehicles on schedule. Additionally, it ensures they are complete within cost targets.
Once you start this process, it becomes clear that effective project control practices should be tailored to the specific needs of each industry. But this is not without challenges. Next up, let’s cover some of the problems you might face as you implement project controls.
Challenges in project control
Overall, project controls are essential for project success, but project managers face challenges. So, let’s take a look at a few of these challenges and prepare you for what lies ahead.
- Resource management: This challenge involves ensuring that project resources are adequately allocated and utilized to meet project requirements and deadlines.
- Scope creep: Scope or budget creep presents a challenge by causing the project scope to expand gradually, potentially leading to project delays and increased costs.
- Budget constraints: Budgets challenge project managers to achieve project goals and deliverables within the allocated financial resources, necessitating careful cost management and prioritization.
- Tight schedules: Quick turnarounds create pressure to complete tasks within stringent timeframes, requiring efficient time management and scheduling to prevent delays.
- Unforeseen risks: Unpredictable risks introduce unexpected events or circumstances that can disrupt project progress and require prompt and effective mitigation strategies to minimize their impact.
Managing these risks through proactive planning, monitoring, and mitigation strategies is crucial for ensuring project success.
The future of project control
As technology evolves, project control is bound to grow in the coming years. AI and ML methodologies are bound to make their way into project processes, enabling project managers to predict project outcomes and identify risks. Overall, AI will help improve resource and cost allocation for projects.
In 2024, organizations have embraced Agile methodologies. Next, project control must continue to evolve while focusing on innovation.
Conclusion
To sum up this post, one thing is clear: Project control is crucial for a project manager to ensure project success.
However, effective project control requires more than just understanding the concept—it demands the right tools and strategies. This is where project cost tracking software plays a vital role. By providing real-time insights into budgets, expenses, and labor costs, it helps project managers maintain control, prevent overspending, and drive profitability.
Lastly, in addition to the techniques in this article, it is crucial to find the right tools to enhance efficiency, improve outcomes, and achieve the project goal. Hubstaff drives productivity for work teams by automating time tracking processes, workforce management, and productivity metrics, making it a one-app solution for project control.
Most popular
The Critical Role of Employee Monitoring and Workplace Security
Why do we need employee monitoring and workplace security? Companies had to adapt fast when the world shifted to remote work...
15 Ways to Use AI in the Workforce
Whether through AI-powered project management, strategic planning, or simply automating simple admin work, we’ve seen a dramatic...
The AI Productivity Panel: Lessons From Leaders on What’s Working (and What’s Not)
When I moderated this AI productivity panel, I expected a solid conversation. What I didn’t expect was the flood of real-world i...
Employee Performance Dashboards: Templates, Tools, and Best Practices
Keeping track of how your team’s really doing can be tricky. Spreadsheets pile up, one-on-ones only tell part of the story, and...