We’ve all wondered about the ideal payroll frequency before. Is it better to get paid weekly or biweekly?
Whether you’re an employee pondering this question or an employer searching for the optimal payroll schedule, we’ve got your back. Let’s explore the options together.
- Weekly pay: Employees get a paycheck every week, offering more frequent access to funds but in smaller amounts.
- Bi-weekly pay: Employees receive paychecks every two weeks, with more money per paycheck but less frequent payouts.
Which is better? Well, it’s complicated — and the answer will differ for everyone. For employees, this will depend on your finances and budgeting. For businesses, factors like industry norms, employee preference, and cash flow are the main considerations.
Let’s unpack the nuances of these two common payroll frequencies.
Boost your team’s efficiency with Hubstaff's productivity tools
TL;DR: Is it better to get paid weekly or biweekly?

For employees, getting paid weekly provides more frequent paychecks, which can be beneficial for managing short-term expenses and maintaining a consistent cash flow. On the other hand, biweekly pay results in larger paychecks, making it easier to budget for extended periods.
For business owners, biweekly pay can streamline administrative processes and reduce costs with fewer processing cycles, while weekly pay provides more frequent disbursements, aligning with specific budgeting preferences and offering consistent cash flow.
The overall winner: The resounding opinion is that biweekly payroll works best for most businesses and employees.
The U.S. Bureau Of Labor Statistics found that a biweekly pay schedule is the most common payment frequency in the private sector. According to the BLS, 43% of businesses in the U.S. pay their employees biweekly, while 27% pay their employees weekly.

Of course, just because something is popular doesn’t mean it’s the right choice for your personal finances or your business. Let’s examine the pros and cons of weekly vs. biweekly pay, first from an employee’s perspective and then from a business perspective.
Biweekly vs. weekly pay for employees
The choice between getting paid weekly or biweekly can significantly impact your finances, so understanding how biweekly vs. weekly pay factors into your budget is essential. Here are the key considerations as we see them.
Cash flow management
Money in, money out – managing cash flow is a big deal. The frequency of your paychecks is crucial in navigating your cash flow.
- Weekly payroll: Getting paid on a weekly basis gives employees quick access to funds, perfect for handling those immediate needs and short-term expenses. This system may work best for hourly employees or seasonal employees.
- Biweekly payroll: Biweekly payroll requires more budgeting finesse since it’s less frequent. But when the paycheck hits, it’s a substantial sum, great for larger expenses like bills, rent, or mortgage payments.
Overtime impact
The calculation and impact of overtime pay differs between weekly and biweekly paychecks due to the frequency of pay periods.
- Weekly payroll: Weekly paychecks may be impacted more by overtime calculations. Weekly payroll ensures a quicker payout for overtime if an employee works extra hours one week and fewer hours the next.
- Biweekly payroll: Overtime may result in more substantial additions to a biweekly paycheck as the overtime earnings accumulate over a two-week period.
Ultimately, the “better” option depends on individual financial goals, spending habits, and the ability to budget effectively with different pay frequencies.
Budgeting
Everyone budgets differently. The way you build a budget can also impact how often you want to get paid. Overall, biweekly budgeting works best for most people, but there are perks to weekly pay.
- Weekly payroll: Offers a more frequent influx of smaller amounts for those who prefer steady, weekly budgeting. This can be beneficial for those with a tighter budget.
- Biweekly payroll: Provides larger sums less frequently, which is suitable for those who prefer managing finances over a more extended period. Additionally, there are some months where a biweekly pay period means that employees receive three paychecks in one month.
You might be doing a double take if you haven’t been on a biweekly pay cycle before. But you did read that correctly. With a biweekly pay cycle, occasionally, employees receive three paychecks per month. Don’t worry, we’ll explain.
Why do employees sometimes receive three paychecks in a biweekly pay period?
Employees receive three paychecks in a month with a biweekly pay schedule due to the misalignment between the traditional calendar month and the biweekly pay period.
Here’s how it works:
A year consists of 52 weeks, but a calendar year has slightly more than 52 weeks (365 days divided by seven days per week equals 52.14 weeks).
In a biweekly pay system, employees receive 26 paychecks in a year (52 weeks divided by 2).
Since a calendar month is not exactly two weeks, there are occasional months where the extra days result in three biweekly pay periods instead of the usual two.
This happens twice a year when there are months with 31 days, and the extra days create a scenario where three biweekly pay periods fall within that month.
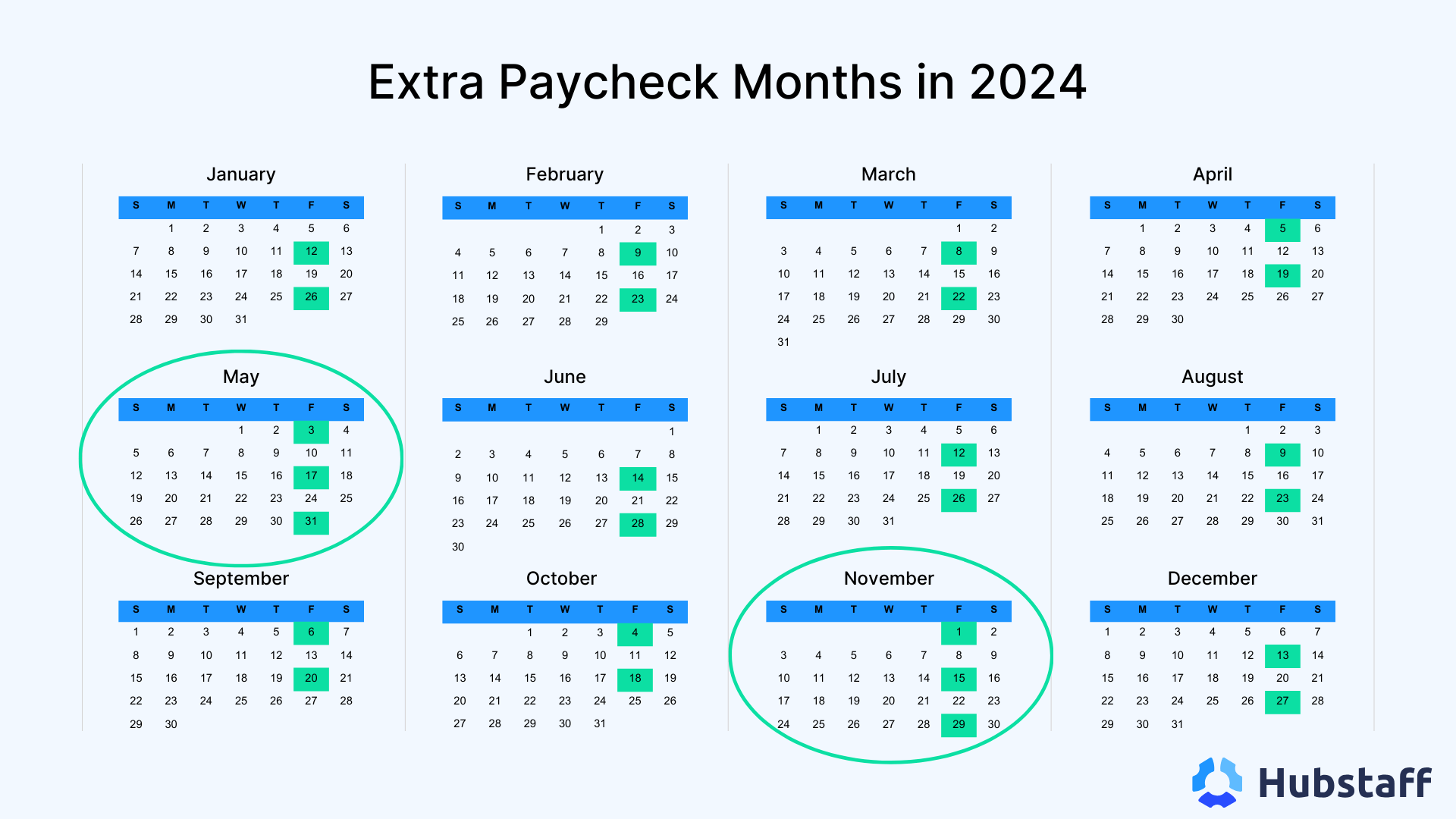
This is one reason that some employees prefer the biweekly pay period over a weekly pay period. Though you’re not getting more money annually, the way this payment model can impact your budgeting can feel like a perk.
Biweekly vs. weekly pay from an employer’s perspective
Navigating the intricacies of payroll is a strategic decision for employers, too. Just as it does for employees, choosing between weekly and biweekly payments holds considerable weight for employers as well.
Let’s examine the key considerations employers need to factor into this decision-making process.
Cash flow management
The choice between weekly and biweekly pay schedules significantly impacts cash flow management. Here’s how each program affects cash flow:
- Weekly payroll: Requires more frequent disbursements, impacting cash flow more regularly. This can create a challenge for businesses, as cash is consistently leaving the company — sometimes at a faster rate than it’s coming in.
- Biweekly payroll: Provides a more predictable cash flow as payments are made less frequently. This pay structure is popular with large companies with more than 1,000 employees.
Administrative efficiency
The choice between weekly and biweekly payments also influences administrative efficiency. How often you process payroll is a significant consideration that leads business owners to prefer paying employees biweekly.
- Weekly payroll: Involves more frequent payroll processing, potentially increasing administrative workload. However, weekly pay periods coincide with the workweek, allowing seamless compliance with FLSA overtime pay laws.
- Biweekly payroll: Weekly pay means running payroll, managing tax withholdings, and administering benefits 52 times annually. Since the biweekly model has only 26 pay periods, you’ll save considerable admin time going this route.
Costs and resources
Every payroll schedule comes with costs and will require different resources and coordination from your billing team.
- Weekly payroll: Weekly pay may incur higher administrative costs due to increased processing frequency. Administering weekly wages can be time-consuming, especially for large companies.
- Biweekly payroll: As mentioned above, biweekly payroll requires less time and administrative work and can help you save on overhead costs. Payroll costs are typically lower with biweekly pay.
Budgeting and financial planning
Businesses must ensure their chosen pay frequency aligns with budgeting preferences and company financial planning.
- Weekly payroll: Weekly payroll suits businesses managing finances every week, offering a more granular approach. However, weekly pay increases the effort necessary to administer tax withholdings, employee benefits, paid time off, and holidays.
- Biweekly payroll: Allows for planning with more significant sums over a slightly extended period. However, since some months will have three paydays, this may complicate the bookkeeping process. Companies may struggle to meet the extra payrolls that occur twice a year without adequate planning.
Like any decision, it’s important you tailor payroll decisions to your business’ specific circumstances and priorities, considering financial and human resource factors.
Other payroll options
Choosing how often employees get paid isn’t just a payroll detail; it’s a decision that can affect everyone’s wallets and overall happiness.
If weekly or biweekly payroll doesn’t feel like the right fit for your team, here are some other options to consider.
A breakdown of payroll options
- Daily payroll: Daily payroll means getting paid for the day’s work, providing quick access to earnings. It’s common in gigs or daily jobs, like construction or events. While it’s a win for immediate cash, daily processing can be a challenge for employers. They need solid systems to handle the constant payouts and must stay on top of cash flow to make it work. In industries with flexible schedules, though, daily payroll offers a real-time financial perk for employees.
- Semi-monthly: Semi-monthly payments refer to a payment frequency occurring twice a month, typically on specific dates such as the 15th and the last day of the month. This payment schedule is used by employers to balance between the more frequent weekly payments and the less frequent bi-monthly payments.
- Monthly payroll: Opting for monthly payroll streamlines things on the employer side, simplifying admin tasks. However, it can be tricky for employees to manage monthly budgets. They might need extra financial support to navigate the longer gap between paychecks. Managing this approach also means staying on top of cash flow to meet the more significant lump-sum payment at month-end.
- Quarterly payroll: With quarterly payroll, employees receive pay each quarter (every three months). This approach suits certain businesses where the workflow and cash flow align with the quarterly rhythm, offering a less frequent but more predictable schedule for managing payroll tasks and budgeting.
When businesses pick how often they pay their folks, it’s a balancing act where you have to consider:
- Cash flow
- Simplifying admin work
- Employee well-being
- Industry standards
The key is finding the sweet spot for everyone in the company.
How do you decide what payroll system is right for you?
For business owners, choosing a payroll schedule that works for your business is critical to maintaining financial health. By considering the pros and cons of weekly versus biweekly pay schedules, you can optimize your payroll system for your employees and your company’s operational needs.
Here are some key considerations to think about before making your final decision.
Key considerations
- Legal compliance: When figuring out your payroll schedule, it’s not just about what’s convenient. You’ve got to play by the rules. Different countries and even states have laws about how often you need to pay your people. In the U.S., employers must follow the Fair Labor Standards Act and other tax and labor laws.
- Employee preferences: Consider surveying employees to understand their priorities for more frequent, smaller paychecks (weekly) or larger, less regular paychecks (biweekly). Sending out an anonymous survey is a great way to get unbiased feedback from your team. Creating an employee handbook with payroll details and an anonymous survey is a great way to get unbiased team feedback.

- Industry norms: Checking out industry standards helps you figure out if there’s a common pay frequency that makes sense for your business. This lets you learn from the mistakes and experiences of other businesses in your network. Plus, your team is likely accustomed to the common pay frequency in their industry.
- Effect on overtime and bonuses: When you pick how often your team gets paid, it’s not just about the regular paycheck. Think about how it plays into overtime, bonuses, and commission, too. Depending on whether it’s weekly or biweekly, it could affect how these extras get calculated and handed out.
Impact on seasonal variations: When contemplating the choice between a weekly or biweekly payroll schedule, it’s crucial to analyze how your business navigates through seasonal variations. Assessing which payment frequency accommodates these fluctuations more effectively ensures that your payroll system remains resilient despite varying workloads.
The decision should be tailored to the business’s specific circumstances and priorities, taking financial and human resource considerations into account.
Key takeaways
It’s important to carefully select which payroll schedule will work best for your business and employees.
- Biweekly pay is the most popular payroll schedule in the U.S., but that doesn’t mean it’s the right fit for everyone. Businesses tend to prefer biweekly payroll because it saves money in payroll processing. Employees like that biweekly pay amounts to several “extra” paychecks a year, but this is just personal preference.
- Talk to your employees and read the biweekly vs. weekly pay section from an employee’s perspective. Finding the right balance between benefiting your business and your employees is critical. In fact, almost half of U.S. workers consider leaving the company after experiencing two payroll issues.
- Once you find the right schedule, you are required to stick to it in the United States. In the U.S., Federal law mandates consistent pay frequency throughout the calendar year. You’ll want to carefully read over the State Payday Requirements for your location before making any final decisions.
- Once you find your ideal payroll schedule, use software like Hubstaff to automate your scheduling and payroll administration. Hubstaff has integrations with popular payroll software solutions for better bookkeeping, so you or your Human Resources team can be confident they are processing payroll accurately.
As a manager, the decision comes down to you. With the right payroll schedule, you can keep your employees happy, manage your cash flow, and focus on growing your business.
Do you have an opinion on biweekly or weekly payroll you’d like to share? Have you found an alternative model that works better than both? Let us know!
Most popular
The Fundamentals of Employee Goal Setting
Employee goal setting is crucial for reaching broader business goals, but a lot of us struggle to know where to start. American...
Data-Driven Productivity with Hubstaff Insights: Webinar Recap
In our recent webinar, the product team provided a deep overview of the Hubstaff Insights add-on, a powerful productivity measurem...
The Critical Role of Employee Monitoring and Workplace Security
Why do we need employee monitoring and workplace security? Companies had to adapt fast when the world shifted to remote work...
15 Ways to Use AI in the Workforce
Whether through AI-powered project management, strategic planning, or simply automating simple admin work, we’ve seen a dramatic...




