In the ever-evolving landscape of modern work, the ability to track employee performance has undergone a remarkable transformation.
Employee performance data provides valuable insight into how an employee is doing at any given time. However, the phrase itself is an umbrella term. Various metrics offer insight into how an employee performs in their position, such as views in quality, quantity, and efficiency.
Tracking employee performance is a cornerstone of effective management, but it’s not without hurdles. The challenges of performance tracking extend beyond mere clock-watching. From the intricacies of remote work to the quest for comprehensive and meaningful metrics, organizations grapple with multifaceted challenges.
As organizations embrace remote work and seek to harness their workforce’s full potential, traditional performance assessment methods are being reimagined. No longer confined to merely counting work hours, the focus has shifted towards a more nuanced and results-driven approach.
In this article, we’ll delve into the vital importance of tracking employee performance, unveil optimal strategies for monitoring productivity, and provide an insightful breakdown of the key performance metrics every professional should be well-versed in.
Boost your team’s efficiency with Hubstaff's productivity tools
Why is employee performance data important?
As mentioned above, employee performance data is critical to track because it provides a measurable way to see how team members work in their current positions at a given time. With this data, companies can further support employee growth and development by providing data-driven feedback and encouragement.
Collecting and analyzing this data with an employee helps ensure they work and operate as the company expects. Having this information on file also allows a company to look back at past months or years and determine if their employees are making the positive progress they should be.
The importance of regular employee reviews
Each company tracks and provides feedback for an employee’s performance differently, based on what works best with their structure. Companies can choose between holding monthly, quarterly, or annual reviews and determine whether a direct manager, a human resources team, or another party completes these performance reviews.
Giving feedback guarantees that employees are routinely in contact with their managers. This setup supports regular communication and allows managers to check on employees, specifically for signs of burnout. Additionally, when the employees perform to the best of their ability and in line with expectations, it helps ensure they are working to meet company goals.
Employee performance tracking helps both the employee and the company in this sense. However, we’ll get into even more benefits of employee performance tracking next.
Track employee productivity
Get automated activity rates, late or missed shift data and more from Hubstaff.
Benefits of tracking employee performance metrics
The most significant benefit of tracking employee performance is that employees know what is expected of them. With a clearer understanding of what to do, employees know when they cannot meet expectations and can comfortably vocalize any concerns to their managers.
- Accountability: Tracking the performance of employees cultivates a sense of responsibility.
- Improve staffing: Analyzing this data can highlight areas of strength and weakness among an employee’s abilities. With this information, managers or HR teams can assist employees with relevant resources or classes or intentionally assign future tasks around their strengths.
- Enhance employee experience: Performance metrics elevate the employee experience because employees can work on projects they know they can excel at and feel supported in the areas they want to grow. It also helps increase employee retention because they are more confident and excited about their day-to-day work.
- Increase productivity: By having a measurable performance value, employees will intentionally work harder to surpass their previous performance statistics. Performance statistics allow employees to compete with themselves for improved output.
Psychological aspects of performance evaluation
Constructive feedback and recognition are powerful catalysts for improving employee performance and boosting morale. Constructive feedback provides employees with specific insights into their strengths and areas for improvement, enabling them to set clear goals and develop their skills.
When delivered effectively, feedback promotes a growth mindset. It fosters a culture of continuous learning — additionally, recognizing employees for their accomplishments, whether big or small, reinforces positive behavior and motivates them to excel. Recognition cultivates a sense of appreciation and belonging, supporting the idea that their contributions are valued.
Transitioning to nuanced performance tracking
Performance tracking has evolved significantly from merely counting work hours. In the industrial age, hours worked were the primary measure of productivity. However, the digital age and the shift to knowledge work have changed the game.
Modern productivity is about outcomes, quality, and meeting specific goals. Performance tracking now involves data-driven assessments, project progress, and individual contributions, emphasizing the value an employee brings to the organization.
The rise of remote work has further fueled this evolution, focusing on results and adaptability rather than just hours worked.
How do you measure employee performance?
The three main types of metrics companies typically track are quality, quantity, and efficiency.
- Quality: track with client or customer surveys that provide feedback on areas like the likelihood of a customer recommending this company to others.
- Quantity: calculate by using a daily log sheet or task management platform.
- Efficiency: monitor digitally or manually by combining the metrics gathered in the quality and quantity areas.
Measuring employee performance has also become more accessible due to a range of task management software and online communication platforms that serve to store and analyze this data for companies.
When is the best time to measure employee performance?
All companies should track employees’ performance metrics year-round to ensure adequate and consistent data for their employees. However, there are some crucial moments during which managers will want to look closely at performance data.
Annual reviews
It’s up to the company to determine whether they will conduct annual performance reviews or opt for monthly or even weekly check-ins. Examining and critiquing the data is essential so managers and employees have a good idea of their capabilities and progress.
Onboarding
The performance appraisal process begins during employee onboarding. Managers must clarify the performance goals and company standards so employees are prepared and in the loop. Since the expectations are set early on, employees know who and how to ask for help if they need clarification. Additionally, knowing what’s expected of them prevents anyone from being blindsided when it comes time for the employee performance reviews.
Regular check-ins
In addition to these formal and scheduled reviews, it’s essential to maintain frequent check-ins between employees and their managers. These unofficial chats help measure job satisfaction and allow managers to assist employees in reaching their goals. They also present a good time for small performance reviews instead of waiting for the following formal review.
How to employ frameworks for goal-setting
Frameworks like OKRs, KPIs, and SMART goals are powerful tools for setting clear and achievable goals while effectively measuring performance. The organization’s goals should be made clear to employees working on projects, and managers should consider these goals when they delegate tasks.
- KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are specific metrics or data points organizations use to measure and evaluate their performance in critical areas. KPIs provide a clear and quantifiable way to assess progress towards meaningful goals and objectives, enabling informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
- OKRs (Objectives and Key Results): OKRs are a goal-setting framework that fosters alignment and transparency within organizations. This framework encourages employees to set challenging but attainable goals and ensures that those goals are tied directly to the organization’s overall mission and strategy.
- Objectives are high-level, ambitious goals.
- Key Results are specific, measurable steps that indicate progress toward those objectives.
- SMART Goals: SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This framework ensures that goals are well-defined and practical.
- Specific goals are clear and concise.
- Measurable goals can be tracked and quantified.
- Achievable goals are realistic and attainable.
- Relevant goals are aligned with broader objectives.
- Time-bound goals have a deadline.
Both OKRs and SMART Goals are integral to performance measurement and management, offering clarity and structure to the goal-setting process. They facilitate tracking and assessing progress, ensuring that employees and organizations remain aligned and focused on achieving objectives while maintaining accountability and driving productivity.
Now, let’s discuss the essential performance metrics managers need to know.
5 essential employee performance metrics
These five metrics provide a cohesive set of employee performance measurements that addresses all the vital areas. As stated above, these performance indicators must be collected year-round for a complete overview of employee work abilities.
1. Goal-based metrics
A goal-based metric clearly defines how a company achieves goals. This metric also translates whole company goals into specific plans tailored to an employee’s role, as goal-based metrics vary drastically based on an employee’s responsibilities. Goal-based metrics also follow the management technique by objective, where companies or employees set clear goals for a constrained time frame and meticulously monitor their progress in meeting them.
An example of a goal-based metric for a salesperson role is to close 20 sales per month. The salesperson can then figure out roughly how many customers they need to speak to to hit this goal. If about 1 in 5 customers purchase a product, they know they need to talk to about 100 people each month to reach their goal of 20 items sold. Managers must help employees properly set relevant goals for each team member.
One technique for goal-setting is to ensure each goal can be directly tied back to a business need, allowing employees to see how their own work contributes to the company’s success.
2. Efficiency & effectiveness metrics
Time management and task completion tracking can help measure efficiency and effectiveness. Time management would include task completion times and your employee’s ability to complete all their work. Managers can create different metrics for specific roles, but some measurable examples would be on-time attendance and on-time task performance. On the other hand, on-time task completion would determine if employees finish their responsibilities on or before due dates. It could be measured by evaluating the frequency of late projects.
3. Metrics pertaining to quality of work
Another essential metric includes looking at the quality of work. One strategy for ensuring quality in employees’ work is having an assigned quality assurance (QA) team member oversee the work itself and spot errors. Another approach is through a client/customer survey, like a net promoter score, that evaluates the satisfaction of key stakeholders.
A net promoter score is used to gauge customer experience and is calculated simply through a one-question market research survey. For example, businesses might prompt retail store or restaurant customers to complete a survey asking how likely they are to recommend the service or product to a friend. This measure of satisfaction reflects the quality of work an employee delivers because their role directly impacts the customer experience.
Having a long-term running log of an employee’s quality performance can be beneficial during performance evaluations to highlight employee-specific strengths and weaknesses. Managers can also use workforce analytics software to highlight where a team member might need more assistance, guidance, or training.

4. Personal growth goals
In addition to having goals set by the company, it is instrumental that employees are encouraged to develop personal objectives. Companies can also promote the development of individual goal-setting by having company employee performance metrics that gauge it, such as the number of goals completed or time spent on personal goals.
5. Training & continuing education metrics
In addition to their typical work functions, many companies offer training or continuing education opportunities.
Some examples of related metrics a company could evaluate are the number of training programs attended, how much content employees retain from the training, and how well the employee integrates the content into their work processes.
Taking the extra time to do so is worth it for the company to help highlight the employees who are eager to better themselves and the organization.
Evaluating employee performance data
Each of the metrics discussed above helps evaluate employee performance. The five metrics capture and measure different aspects of an employee’s ability and provide a cumulative and holistic view of their overall performance.
Managers should collect feedback and productivity data and track performance throughout the year. Managers or the employee’s team lead can review team member’s progress during designated performance review times to provide consistent and actionable feedback.
Setting performance standards and individual goals
Having individual goals catered to personally identified areas of improvement creates initiative and shows employees that the company cares about their growth. Setting achievable goals and tracking them independently also indicates the company an employee’s eagerness to learn and advance their career.
Establishing clear performance expectations and setting individual employee goals is fundamental to ensuring everyone is aligned with the organization’s objectives. Clear expectations provide a roadmap, helping employees understand what is expected of them and how their work contributes to the company’s success.
Exploring tools for measuring employee performance
In today’s dynamic work environment, tracking and optimizing employee performance is paramount for organizational success. Fortunately, many powerful tools are available to streamline this process and enhance productivity.
Hubstaff
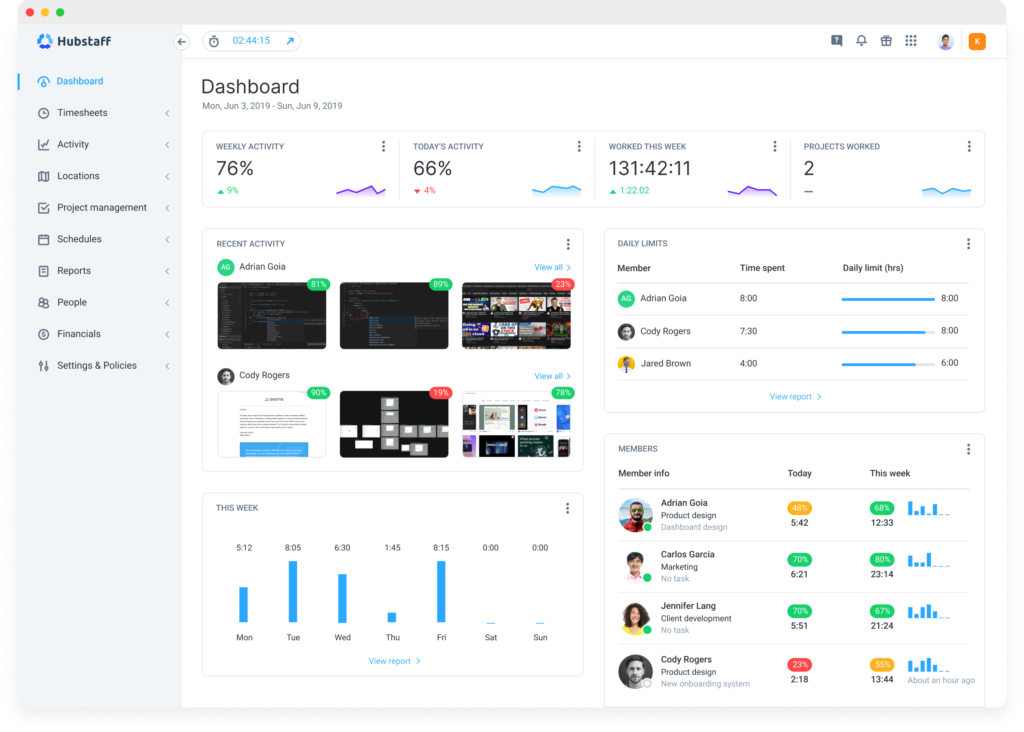
- Features: Hubstaff offers time tracking, productivity monitoring, and employee activity tracking. It also provides detailed reports on time spent on tasks and projects, with optional screenshots and activity levels.
- Utilization: Hubstaff helps managers monitor productivity, track project progress, and allocate resources efficiently. It also offers integrations with other project management tools for a holistic view of performance.
Workday
- Features: Workday is an enterprise-level HR and finance management platform that includes performance management, time tracking, and workforce planning.
- Utilization: Workday is used by large organizations to track employee performance, align workforce planning, and manage HR functions efficiently.
BambooHR
- Features: BambooHR is an HR software that includes time tracking, employee self-service, and performance management.
- Utilization: BambooHR helps HR departments track employee performance, manage time-off requests, and streamline HR processes.
Zoho People
Features: Zoho People is an HR management system that includes time tracking, attendance management, and performance appraisal.
Utilization: Zoho People is helpful for HR departments to track employee attendance, manage timesheets, and conduct performance appraisals.
These tools offer a range of features to track employee performance, manage tasks, and improve project outcomes. Depending on your organization’s needs and size, you can choose the tool that best aligns with your goals and processes.
How to use tools to track employee performance
Empower self-monitoring
Self-monitoring tools empower individuals to assess and enhance their performance. Hubstaff allows users to monitor their work hours, track productivity, and analyze their activity levels, facilitating a clear understanding of how they allocate their time and identify areas for improvement.
In addition to Hubstaff, there are several other self-monitoring tools and strategies available:
- Goal-setting apps: Platforms like Todoist and Notion enable users to set and monitor personal and professional goals, ensuring they stay on track toward achievement.
- Calendar apps: Tools such as Google Calendar and Microsoft Outlook assist users in scheduling and managing their time efficiently, reducing scheduling conflicts and improving productivity.
- Project management apps: A project management tool like Asana or ClickUp can help employees monitor their own work and performance metrics.
- Training and skill development: Enrolling in online courses or workshops to enhance existing skills or acquire new ones is another valuable self-monitoring strategy.
By utilizing these self-monitoring tools and strategies, individuals can actively assess their performance, identify areas for growth, and optimize their efficiency in both professional and personal endeavors.
Use productivity scores
A productivity score is a quantitative measure that assesses an employee’s or team’s efficiency and effectiveness in completing tasks, projects, or assignments. It aims to provide a transparent and objective evaluation of work performance and resource utilization. Productivity scores are especially useful for remote employees and hybrid teams looking to monitor employee performance while they are working remotely.
Employee tracking software like Hubstaff can assist in this metric collection process by automatically tracking, storing, and sorting a team’s productivity data, including activity rates, late or missed shifts, and more. Some tools even offer a way to compare productivity rates amongst similar roles or industries to give you more explicit benchmarks.
Use charts and visuals for performance data
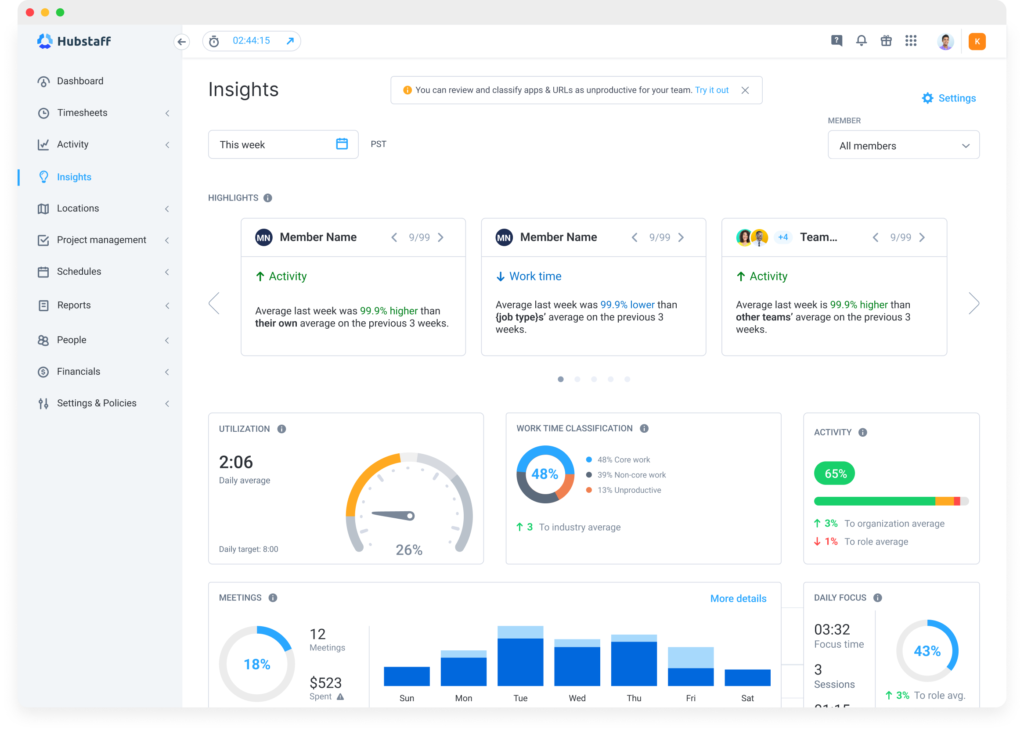
Utilizing charts and visuals to convey performance data streamlines data interpretation, revealing trends and patterns at a glance. These graphics simplify data communication and facilitate data-driven decision-making across various industries and audiences.
At Hubstaff, we understand that charts and visuals for performance data offer a dynamic and insightful way to comprehend and monitor productivity. With various customizable charts and graphs, we enable users to visualize their team’s work patterns, track time spent on tasks, and assess activity levels at a glance.
These visual representations help managers and team members quickly identify trends, performance patterns, and areas for improvement. Hubstaff’s intuitive visualizations transform raw data into actionable insights, fostering more informed decision-making and enhancing overall organizational performance management.
Key takeaways
In today’s evolving work landscape, tracking employee performance has grown significantly. Employee performance data, encompassing quality, quantity, and efficiency metrics, offers valuable insights.
However, the challenges extend beyond clock-watching, especially in the remote work era. Traditional performance assessment methods have given way to a more nuanced and results-driven approach, focusing on outcomes, quality, and goal achievement.
Performance metrics, including goal-based, efficiency, quality of work, personal growth, and training metrics, are vital for evaluating and improving performance, fostering accountability, enhancing employee engagement, increasing productivity, and supporting individual development.
As businesses navigate the dynamic work environment, combining these strategies, metrics, and tools ensures a holistic approach to tracking and improving employee performance, contributing to organizational success. Start tracking employee performance today to see the difference it makes in personal productivity and completed tasks.
Subscribe to the Hubstaff blog for more posts like this
Most popular
The Fundamentals of Employee Goal Setting
Employee goal setting is crucial for reaching broader business goals, but a lot of us struggle to know where to start. American...
Data-Driven Productivity with Hubstaff Insights: Webinar Recap
In our recent webinar, the product team provided a deep overview of the Hubstaff Insights add-on, a powerful productivity measurem...
The Critical Role of Employee Monitoring and Workplace Security
Why do we need employee monitoring and workplace security? Companies had to adapt fast when the world shifted to remote work...
15 Ways to Use AI in the Workforce
Whether through AI-powered project management, strategic planning, or simply automating simple admin work, we’ve seen a dramatic...